High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) is a critical advanced nuclear fuel for next-generation nuclear reactors, including small modular reactors (SMRs) and Generation IV reactors. This guide explains HALEU definition, HALEU production, HALEU benefits, and its role in nuclear energy and energy independence.
What Is HALEU?
High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) is uranium enriched to 5%–20% uranium-235 (U-235), higher than traditional low-enriched uranium (LEU) (<5% U-235) but below highly enriched uranium (HEU) (>20% U-235). This nuclear fuel enrichment level optimizes reactor performance while minimizing proliferation risks per IAEA standards.
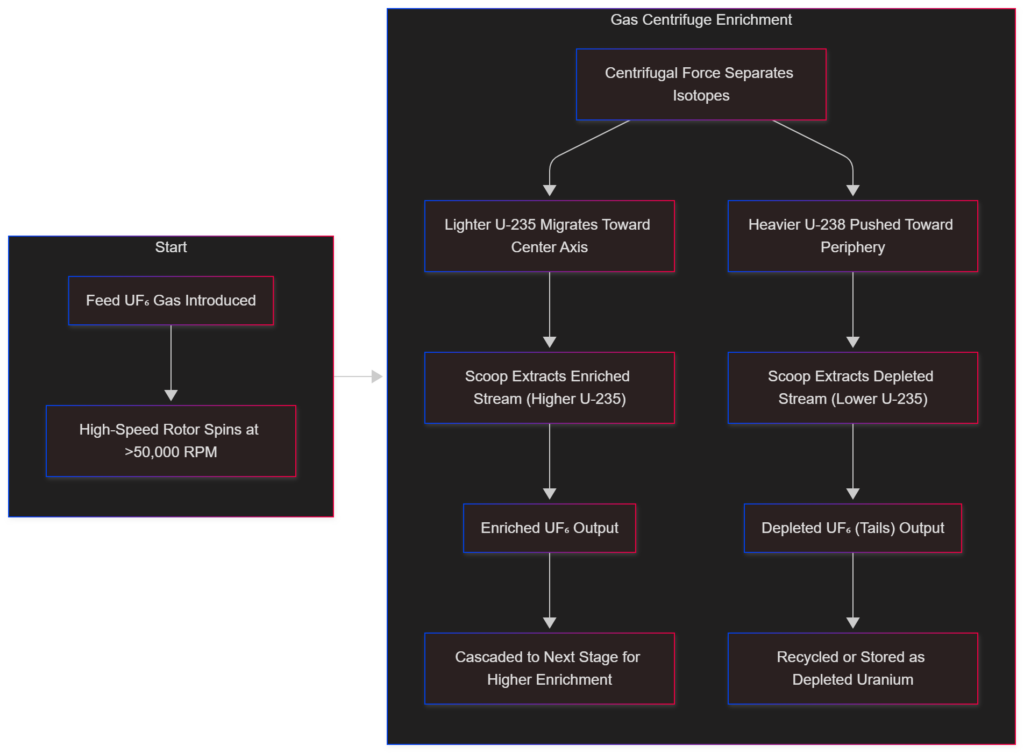
HALEU Production Process
HALEU production follows the nuclear fuel cycle:
- Uranium mining and conversion to uranium hexafluoride (UF₆).
- Gas centrifuge enrichment to target 5%–20% U-235 from natural uranium, re-enriched tails, or down-blended HEU.
- U.S. HALEU initiatives: DOE’s HALEU Availability Program aims for 20 metric tons/year by 2027, with demos at Centrus Energy in Piketon, Ohio.
Key challenges: higher enrichment costs and specialized handling, offset by scaling advanced reactor fuel production.


Top HALEU Benefits for Advanced Nuclear Reactors
HALEU fuel unlocks advantages for SMRs, microreactors, and Gen IV reactors:
1. Superior Reactor Efficiency
- Burnup >100 GWd/t (vs. 40–60 GWd/t for LEU), enabling 10–20-year cores.
- Compact designs for factory-built SMRs.
- Better neutron economy in molten salt reactors or fast reactors.
2. Enhanced Nuclear Safety
- Passive safety systems and negative reactivity.
- TRISO fuel particles for extreme containment.
3. Environmental Advantages
- 50% less spent nuclear fuel.
- Actinide transmutation in fast-spectrum designs.
- Carbon-free baseload power.
4. Economic and Deployment Gains
- Modular nuclear reactors reduce capital risk.
- Lower OPEX via extended fuel cycles.
- Applications in space propulsion and industrial heat.
5. Energy Security and Independence
- Ends reliance on Russia’s 90%+ global HALEU supply.
- Supports domestic uranium enrichment under the Energy Act of 2020.
Overcoming HALEU Challenges
Address HALEU availability, NRC licensing, and public perception through projects like TerraPower Natrium and X-energy Xe-100, plus nuclear policy incentives and allied uranium supply chains.
Conclusion: Why HALEU Matters for Clean Energy
High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium drives advanced nuclear technology, delivering nuclear reactor efficiency, safety, and energy independence. Invest in U.S. HALEU production to lead in sustainable nuclear power and low-carbon energy.


Leave a Reply